
For the past few years, software-as-a-service (SaaS) has become the new norm as more and more companies are purchasing and utilizing the solution in their daily business operations to become more productive, faster, and smarter. For companies that are still confusing between an On-premises and SaaS solution, it is important to consider the more appropriate infrastructure if wanting to gain a competitive advantage over their rivals.
Differences between On-premises and SaaS solutions

An On-premises solution, one of the most common and traditional methods for working with enterprise software, is installed, run, and maintained on computers on the premises of the company using the technology – often in the organization’s data center. It typically requires only a software license from a third-party vendor, while the security, availability, and overall management are the organization’s responsibilities.
On the other hand, SaaS or cloud-computing is hosted and maintained by a third-party provider and is made available to customers over the Internet. Instead of licensed software, the provider gives organizations access to a single copy of an application created specifically for SaaS distribution. These applications help support fundamental business operations, including sales management, customer relationship management (CRM), financial management, human resource management (HRM), etc.
While SaaS is a better option when it comes to enterprises with a massive amount of data thanks to flexible storage scalability, On-premises is preferred for businesses whose security compliance does not allow third-party hosting.
Benefits of cloud-based software
Used to be exclusive to larger companies, SaaS now has made it more affordable for small- and mid-size enterprises (SMEs) and startups as well. Here are the top four reasons for businesses of all sizes to switch from an On-premises system to a cloud-based solution.
1. Cost
While cloud software is priced under a monthly or annual subscription, with no additional hardware investments albeit some fees for support and upgrades; on-premises solutions are priced under a one-time perpetual license fee, based on the size of the organization or the number of users. There are also recurring fees for support, maintenance, and updates. As such, SaaS’s lower entry cost has contributed to its widespread adoption as companies no longer have to pay a huge amount upfront. However, the overtime cost of SaaS will increase and businesses might end up spending more over the course of the system’s life cycle.
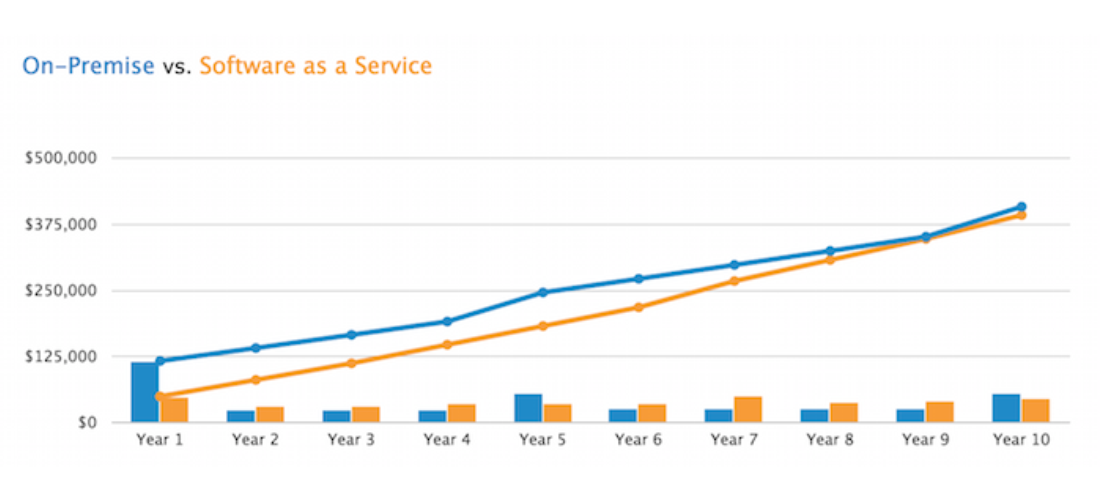
Total costs of ownership in 10 years for cloud-based and On-premises software (Source: Software Advice)
2. Ease of implementation
Speed, time, and ease of implementation are crucial factors impacting the performance and productivity of a company – thus, it is important to consider a solution that satisfies those requirements. Generally, it takes at least one year to build and implement on-premises solutions. As businesses grow, they might have to buy and install more hardware in their data centers, taking more time, human resources, and money. Meanwhile, SaaS software often takes less time to be deployed, either a few months or less than 30 days depending on the complexity of the system. Companies can deploy a cloud-based system across multiple subsidiaries or divisions without having to procure and install IT infrastructure across different sites.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
In order to stay competitive and deliver the best performance to customers, enterprises should sustain flexibility and adaptability, including scalability in cloud computing. A scalable cloud solution can save money over the On-premises alternative considering companies only have to pay for what they need at any given moment, or pay-as-you-go. If the business is growing significantly, they can choose to scale up to increase capacity and maximize performance; if not, they can also scale down the system to minimize wastage of resources and money. On-premises solutions require long-term planning for scaling and are often not suitable for growing businesses as the IT staff has to constantly struggle in the upgrade loop. When the need for scaling arises, the company needs to bear the costs and time associated with the upgrades.
4. Maintenance, support, and updates
Businesses using traditional software have to spend heavily on maintenance and support. Maintaining an On-premises system requires regular backups as well as check-ups to ensure the system is up-to-date. When new functionalities and features are released, the internal IT staff even have to install updates themselves, which is incredibly time-consuming. For cloud-based software, organizations no longer have to install and run applications on their data centers and manage everything by themselves, while eliminating the expense of maintenance, licensing, and support. Updates will be installed in the background by the provider, allowing teams and departments to make informed business decisions with new features right away. Additionally, restoring and data backup are already taken care of by the service provider.
Disadvantages of cloud-based software
Despite significant benefits that allow companies to enhance performance and productivity, cloud-based software also bears certain disadvantages worth identifying before businesses decide to invest in the system.

1. Control and Security
This is one of the main reasons why On-premises software is still the preferable option at the moment, especially for large enterprises and governments. As problems associated with privacy arise, the need for businesses to protect their sensitive data and information also increases. It provides companies the full, direct control and protection over their data, instead of having data stored on 3rd party servers, as compared to SaaS solutions.
2. Connectivity
Since SaaS software is based on web delivery, it requires a strong and stable internet connection. Otherwise, companies will lose access to software and data. This might affect the overall performance and even cause economic damage.
3. Preparing for SaaS Implementation
While it is true that SaaS solutions have made organizations become more productive, without proper preparation it would be challenging for companies to manage and get the full value of the cloud. Start with determining the needs and goals, as well as the financial health of the organization prior to implementing, then evaluate both the pros and cons of SaaS to see if it aligns with the overall strategies. Additionally, companies must train and upskill their existing workforce, walk them through the transition and help them get used to new technologies.
Conclusion

With SaaS, service providers shoulder the burden of cost, software acquisition, and maintenance, while giving companies the ability to scale and adapt to business requirements. Altogether, it is a hassle-free system made to help enterprises maximize productivity and performance and achieve success in a highly competitive era. If the company decides to adopt the technology, it is crucial to consider its characteristics and prepare the workforce and entire organization for the implementation to be as smooth as possible.
——————–
How do you think about this article? Please share it with us via the comment section below.
PRIMUS – FIRST CLASS JOBS ONLY





